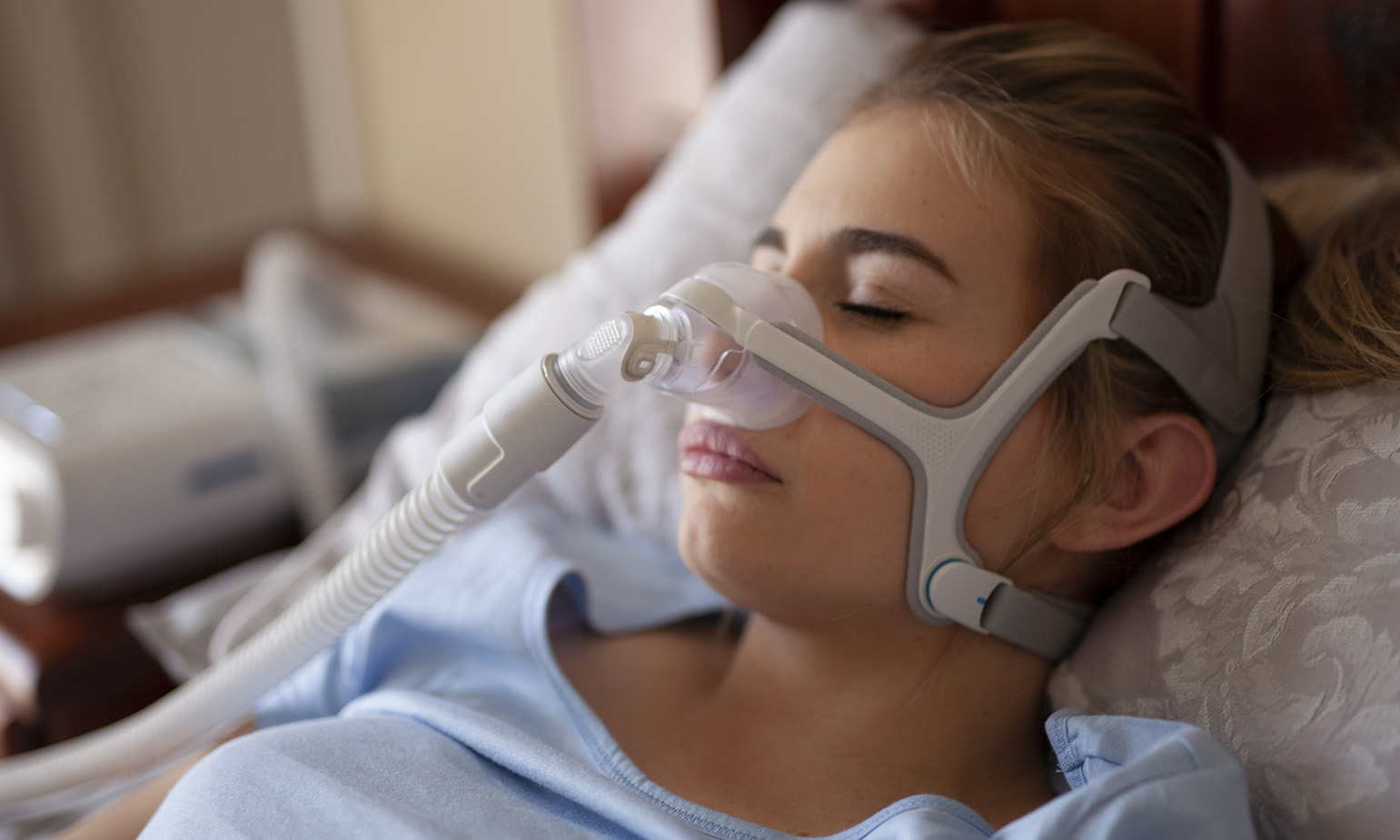
Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) is a disorder that involves a frequent collapse of the upper airways during sleep that results in arousal due to a temporary apnoea, which is the complete cessation of breathing or hypopnoea, a partial blockage of breathing.
What Causes OSA and How Does It Happen?
OSA is one of the most common breathing disorders during sleep. This occurs when the muscles located at the back of the throat relax more than usual. The relaxation of these muscles will result in a narrowed airway and in some cases a complete blockage of the airway. When the airway is obstructed for more than 10 seconds, a buildup of carbon dioxide occurs along with the decrease in oxygen levels of the body.
The brain will detect the impaired breathing and wake the body for a brief period of time, which often goes unnoticed. During this brief arousal, the body will catch its breath with accompanying choking or gasping to reopen the airways. Once the body returns to sleep, the airways collapse again.
Having less than 5 apnoeas per hour of sleep is normal, but in severe cases of sleep apnoea, an individual can have 30 or more apnoeic episodes in an hour. This severe disturbance in sleep indicates that the body is unable to reach the stage of deep sleep which is important for the body’s regeneration and repair.
There are few risk factors associated with OSA.
- Obesity
- Older age
- Chronic nasal congestion
- Abnormal airway or structure of the head
- Dysfunction of the central nervous system e.g. after a stroke
- Neuromuscular diseases e.g. amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Signs and Symptoms of OSA
Experiencing OSA may bring about various signs and symptoms, some of which may be more noticeable by partners than individuals who suffer from OSA. Some of these signs and symptoms include:
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- DIfficulty concentrating during the day
- Headaches in the morning
- Sudden waking by gasping or choking
- Dry mouth or sore throats on waking up
- Loud snoring
- Episodes of breathing cessation during sleep which are observed by partner
In the long run, these signs and symptoms of OSA can lead to detrimental effects not just on the mind but on the physical body too. Left untreated, these long-term sequelae of OSA can lead to premature death. Most of these effects stem from the lack of oxygen intake during sleep from the obstruction and from the lack of healthy sleep, which includes but are not limited to:
- Mood changes or disorders such as irritability or depression
- Cognitive impairment
- Heart and circulatory problems such as heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol etc.
- Impaired glucose regulation which can lead to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Decreased libido
Diagnosis and Treatment
OSA cannot be diagnosed by clinical symptoms only. Diagnosis has to be made by trained healthcare professionals by doing a formal sleep study. In some cases the sleep study can be done at home, but most of the time a sleep study is performed in a sleep lab. An individual suspected of having OSA will spend the night sleeping with a connected machine that takes a range of measurements such as the heart rate, breathing rate and various other bodily functions during sleep.
Treatment of OSA will depend on the severity of apnoea, general condition of the individual and any specific treatable conditions. Weight loss is a conservative method of treatment for those who are overweight or obese. Discussions with the physician, dietician and nutritionist will be beneficial to arrange a long-term plan. However, weight management is a progressive and gradual process. In cases where interventions are needed more urgently, other methods are adopted to provide more immediate relief.
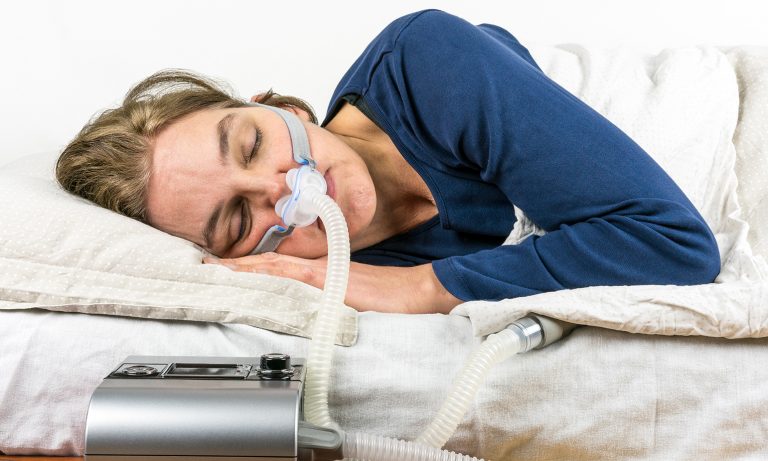
One of these is a device that keeps the airways open during sleep called a continuous positive airway pressure, also known as CPAP. Individuals who are recommended this will sleep with a face mask at night that maintains their breathing throughout the night. Although this method may be uncomfortable at the beginning due to the face mask, it will allow more quality rest and will generally feel better over time.
Other methods include an oral appliance which keeps the airway open but doesn’t work as well as a CPAP. In some rare cases where none of these methods help, surgery may be recommended although it might not be fully effective and there is a chance that the problem may recur.
Conclusion
Obstructive sleep apnoea is not just an inconvenience during sleep, but it can cause many immediate and long-term health problems. Those who are suspected to experience this condition should be evaluated for a formal diagnosis and receive the appropriate treatment to avoid any further progression. Get your Vaccination.

